|
|
|
|
 Far Far |
 WinNavigator WinNavigator |
 Frigate Frigate |
 Norton
Commander Norton
Commander |
 WinNC WinNC |
 Dos
Navigator Dos
Navigator |
 Servant
Salamander Servant
Salamander |
 Turbo
Browser Turbo
Browser |
|
|
 Winamp,
Skins, Plugins Winamp,
Skins, Plugins |
 Необходимые
Утилиты Необходимые
Утилиты |
 Текстовые
редакторы Текстовые
редакторы |
 Юмор Юмор |
|
|
|
File managers and best utilites |
WebSockets. Websocket поддержка браузерами
WebSockets - Web APIs | MDN
WebSockets are an advanced technology that makes it possible to open an interactive communication session between the user's browser and a server. With this API, you can send messages to a server and receive event-driven responses without having to poll the server for a reply.
Interfaces
WebSocket The primary interface for connecting to a WebSocket server and then sending and receiving data on the connection. CloseEvent The event sent by the WebSocket object when the connection closes. MessageEvent The event sent by the WebSocket object when a message is received from the server.- HumbleNet: A cross-platform networking library that works in the browser. It consists of a C wrapper around WebSockets and WebRTC that abstracts away cross-browser differences, facilitating the creation of multi-user networking functionality for games and other apps.
- µWebSockets: Highly scalable WebSocket server and client implementation for C++11 and Node.js.
- ClusterWS: Lightweight, fast and powerful framework for building horizontally & vertically scalable WebSocket applications in Node.js.
- Socket.IO: A long polling/WebSocket based third party transfer protocol for Node.js.
- SocketCluster: A pub/sub WebSocket framework for Node.js with a focus on scalability.
- WebSocket-Node: A WebSocket server API implementation for Node.js.
- Total.js: Web application framework for Node.js (Example: WebSocket chat)
- Faye: A WebSocket (two-ways connections) and EventSource (one-way connections) for Node.js Server and Client.
- SignalR: SignalR will use WebSockets under the covers when it's available, and gracefully fallback to other techniques and technologies when it isn't, while your application code stays the same.
- Caddy: A web server capable of proxying arbitrary commands (stdin/stdout) as a websocket.
- ws: a popular WebSocket client & server library for Node.js.
- jsonrpc-bidirectional: Easy to use asynchronous RPC library with bidirectional calls support over a single WebSocket or RTCDataChannel (WebRTC) connection. The TCP/SCTP/etc. client and server may each host its own JSONRPC.Server endpoint at the same time.
See also
Browser compatibility
We're converting our compatibility data into a machine-readable JSON format. This compatibility table still uses the old format, because we haven't yet converted the data it contains. Find out how you can help!
| Version -76 support | 6 | No support | 4.0 (2.0) | No support | 11.00 (disabled) | 5.0.1 |
| Protocol version 7 support | No support | No support | 6.0 (6.0)Moz | No support | No support | No support |
| Protocol version 10 support | 14 | No support | 7.0 (7.0)Moz | HTML5 Labs | ? | ? |
| Standard - RFC 6455 Support | 43 | 14 | 48.0 (48.0) | 10 | 12.10 | 6.0 |
| Usable in Workers | (Yes) | (Yes) | 37.0 (37.0) | ? | ? | ? |
| Version -76 support | ? | No support | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Protocol version 7 support | ? | No support | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Protocol version 8 support (IETF draft 10) | ? | No support | 7.0 (7.0) | ? | ? | ? |
| Standard - RFC 6455 Support | 4.4 | (Yes) | 11.0 (11.0) | ? | 12.10 | 6.0 |
| Usable in Workers | (Yes) | (Yes) | 37.0 (37.0) | ? | ? | ? |
Gecko notes
WebSockets support in Firefox is continuing to track the evolving WebSocket specification. Firefox 6 implements version 7 of the underlying protocol, while Firefox 7 implements version 8 (as specified by IETF draft 10). Firefox mobile received WebSocket support in Firefox mobile 7.0.
Gecko 6.0
Prior to Gecko 6.0 (Firefox 6.0 / Thunderbird 6.0 / SeaMonkey 2.3), there was, incorrectly, a WebSocket object that some sites were thinking implied that WebSocket services were not prefixed; this object has been renamed to MozWebSocket.
Gecko 7.0
Starting in Gecko 7.0 (Firefox 7.0 / Thunderbird 7.0 / SeaMonkey 2.4), the network.websocket.max-connections preference is used to determine the maximum number of WebSocket connections that can be open at a time. The default value is 200.
Gecko 8.0
Starting in Gecko 8.0 (Firefox 8.0 / Thunderbird 8.0 / SeaMonkey 2.5), the deflate-stream extension to the WebSocket protocol has been disabled, since it's been deprecated from the specification drafts. This resolves incompatibilities with some sites.
Gecko 11.0
Prior to Gecko 11.0, both incoming and outgoing messages were limited to 16 MB in size. They may now be up to 2 GB in size. Note, however, that memory limitations (especially on mobile devices) make that a theoretical maximum, not a practical one. In reality, transfers of that size will fail on devices that don't have enough memory.
Additionally, ArrayBuffer send and receive support for binary data has been implemented.
Starting in Gecko 11.0, the WebSocket API is no longer prefixed.
Document Tags and Contributors
Contributors to this page: goriunov, thwee-alchemist, snuggs, oxygen, chrisdavidmills, jondubois, elithrar, erikadoyle, castis, simon04, alexhultman, webgodo, fscholz, h_ajsf, teoli, EvanDotPro, Sheppy, akiraaisha, arasbm, petersirka, OWaz, jgillich, rvighne, LOVEBOYS, hateka, BYK, allergic, janx, ethertank, torkil, DavidWalsh, Eszett, dynamis, ericz, evilpie, myakura, drawoc, jswisher, Kennyluck, paul.irish, groovecoder, DirkjanOchtman, inma_610, NV Last updated by: goriunov, Mar 29, 2018, 5:46:22 AMdeveloper.mozilla.org
Что такое WebSocket. AJAX или Веб-Сокеты. Асинхронность
Что такое WebSocket. Что лучше — Веб-сокеты или AJAX?
5 (100%) 3 votesWebSocket (Веб-сокет) — это протокол полнодуплексной связи поверх TCP-соединения. То есть с помощью этого протокола можно передавать и принимать сообщение одновременно. Он позволяет в режиме реального времени обмениваться сообщениями между браузером и сервером.
Веб-сокеты уже давно не являются экспериментальными, его используют в браузерных играх, интерактивных системах, платежных система. Веб-Сокеты уже стали частью современного веба!
Браузер — веб-сервер. Как это работает и что нужно менять?
Для веб-разработчиков всегда было проблемой получение реакции браузера на события, который происходит на сервере. HTTP-протокол имеет некие недостатки, и его, наверное, критиковали все разработчики. Один из таких недостатков — это проблема постоянного соединения с сервером. Реализация HTTP-протокола не предполагала подобного рода взаимодействия. Например, если мы хотим получить данные с сервера в браузер, то нужно сделать очередной запрос к серверу, и это предполагает перезагрузку страницы. То есть, если открыли сайт в браузере, загрузили страницу, просмотрели, и к этому времени на сервере изменилось данная страница, то нам нужно перезагрузить страницу, чтобы получить изменение.
Есть довольно большое количество задач, где нам нужно получить асинхронность используя HTTP-протокол. То есть, если на сервер будут изменение, то нужно получить эти изменение в браузере, без перезагрузки. Один из таких примеров — это чат, где люди общаются, и когда один другому отправляет сообщения, то сообщения видна получателю моментально, без перезагрузки страницы. Раньше, создание такого вида приложение было нелегко, находились разные степени интерпретации, которые имитировали push-действия сервера. Один из таких примеров — это организованные на клиенте фреймов, которые перезагружаются раз в секунду и отправляют запросы на сервер.
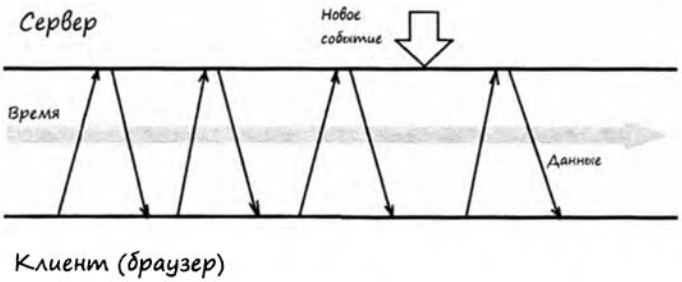
В этом подходе есть много минусов — создается очень большое количество запросов на сервер, тяжело организовать правильную структуру приложений. Я самая главная проблема — это то, что мы делаем эмуляции реакции на серверное событие. Всегда клиент (браузер) получает данные с большой задержкой.
А теперь давайте поговорим об AJAX. Когда объект XMLHTTPRequest появилось в браузерах, положение немного улучшилось. В данном случае мы можем взаимодействовать с сервером по схеме Long Polling. Ниже по пунктам описан суть данной схемы:
- Клиент (браузер) отправляет запрос на сервер,
- Соединение не закрывается и клиент ожидает наступления события,
- Когда события происходит клиент получает ответ на свой запрос,
- Клиент тут же отправляет новый запрос.
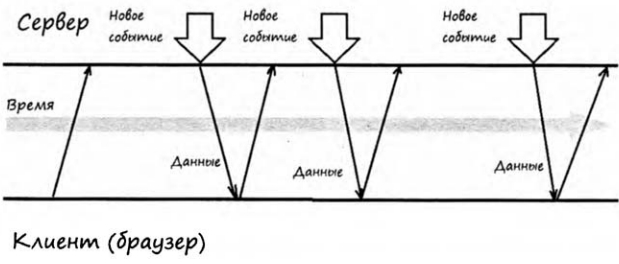
С помощью этого подхода мы получаем асинхронные запросы к серверу, а ответы обрабатываются с помощью функциями обратного вызова. Но и этот подход имеет некоторые недостатки. Главный недостаток этого подхода заключаться в том, что здесь сервер и серверные события не являются инициатором взаимодействия.Не так давно появилось новый протокол, у которого нет таких недостатков, которые выше мы перечислили. Новая технология WebSockets представляет собой реализацию протокола полнодуплексной связи поверх TCP-соединения.
Почему WebSockets? Плюсы и минусы протокола ws
Используя технологию Веб-Сокеты нам нужно забыть привычную систему взаимодействие в мире WWW. Нам нужно забить стандартный модель HTTP-протокола — «запрос/ответ на запрос». В рамках технологии Веб-Сокетов браузер и сервер в любой момент могут отправлять и принимать данные, то ест они становится равными участниками.
WebSocket устанавливает одно единственное соединение клиента с сервером. Для работы с WebSockets обе стороны (клиент и сервер) должны поддерживать данную технологию. Все новые браузеры поддерживают протокол WS, а серверная часть реализуется разработчиком. Когда сервер и клиент готовы к «бою», сервер и клиент могут отправлять через Веб-Сокеты текстовые текстовые сообщение. Передача и прием данных происходит сразу же, данная технология создает двунаправленные каналы связи.
Так как соединение с клиентом и сервером не закрывается (он держится открытым постоянно), это позволяет избежать передачи лишних данных (HTTP-заголовки). В стандарте WebSockets нет никаких ограничение по количеству открытых соединение и по очередностью запросов.
В этом уроке мы узнали — какие способы есть для асинхронных запросов на сервер, что такое WebSocket и какие преимущества у него есть по сравнению с AJAX и HTML фреймов. В следующем уроке мы начнём работать с WebSocket на Node.js, более подробно будем рассматривать данную технологию в действие и напишем чат на Веб-Сокетов и Node.js. Полный список уроков Node.js вы найдете на этом странице.
Похожие статьи
hackerx.ru
WebSocket - Wikipedia
WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011, and the WebSocket API in Web IDL is being standardized by the W3C.
WebSocket is a different TCP protocol from HTTP. Both protocols are located at layer 7 in the OSI model and, as such, depend on TCP at layer 5. Although they are different, RFC 6455 states that WebSocket "is designed to work over HTTP ports 80 and 443 as well as to support HTTP proxies and intermediaries" thus making it compatible with the HTTP protocol. To achieve compatibility, the WebSocket handshake uses the HTTP Upgrade header[1] to change from the HTTP protocol to the WebSocket protocol.
The WebSocket protocol enables interaction between a web client (such as a browser) and a web server with lower overheads, facilitating real-time data transfer from and to the server. This is made possible by providing a standardized way for the server to send content to the client without being first requested by the client, and allowing messages to be passed back and forth while keeping the connection open. In this way, a two-way ongoing conversation can take place between the client and the server. The communications are done over TCP port number 80 (or 443 in the case of TLS-encrypted connections), which is of benefit for those environments which block non-web Internet connections using a firewall. Similar two-way browser-server communications have been achieved in non-standardized ways using stopgap technologies such as Comet.
The WebSocket protocol is currently supported in most major browsers including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari and Opera. WebSocket also requires web applications on the server to support it.
Overview[edit]
Unlike HTTP, WebSocket provides full-duplex communication.[2][3] Additionally, WebSocket enables streams of messages on top of TCP. TCP alone deals with streams of bytes with no inherent concept of a message. Before WebSocket, port 80 full-duplex communication was attainable using Comet channels; however, Comet implementation is nontrivial, and due to the TCP handshake and HTTP header overhead, it is inefficient for small messages. The WebSocket protocol aims to solve these problems without compromising security assumptions of the web.
The WebSocket protocol specification defines ws (WebSocket) and wss (WebSocket Secure) as two new uniform resource identifier (URI) schemes[4] that are used for unencrypted and encrypted connections, respectively. Apart from the scheme name and fragment (# is not supported), the rest of the URI components are defined to use URI generic syntax.[5]
Using browser developer tools, developers can inspect the WebSocket handshake as well as the WebSocket frames.[6]
History[edit]
WebSocket was first referenced as TCPConnection in the HTML5 specification, as a placeholder for a TCP-based socket API.[7] In June 2008, a series of discussions were led by Michael Carter that resulted in the first version of the protocol known as WebSocket.[8]
The name "WebSocket" was coined by Ian Hickson and Michael Carter shortly thereafter through collaboration on the #whatwg IRC chat room,[9] and subsequently authored for inclusion in the HTML5 specification by Ian Hickson, and announced on the cometdaily blog by Michael Carter.[10] In December 2009, Google Chrome 4 was the first browser to ship full support for the standard, with WebSocket enabled by default.[11] Development of the WebSocket protocol was subsequently moved from the W3C and WHATWG group to the IETF in February 2010, and authored for two revisions under Ian Hickson.[12]
After the protocol was shipped and enabled by default in multiple browsers, the RFC was finalized under Ian Fette in December 2011.[13]
Browser implementation[edit]
A secure version of the WebSocket protocol is implemented in Firefox 6,[14] Safari 6, Google Chrome 14,[15]Opera 12.10 and Internet Explorer 10.[16] A detailed protocol test suite report[17] lists the conformance of those browsers to specific protocol aspects.
An older, less secure version of the protocol was implemented in Opera 11 and Safari 5, as well as the mobile version of Safari in iOS 4.2.[18] The BlackBerry Browser in OS7 implements WebSockets.[19] Because of vulnerabilities, it was disabled in Firefox 4 and 5,[20] and Opera 11.[21]
| February 4, 2010 | 4 | 5.0.0 | |||||
| May 6, 2010May 23, 2010 | 4.0 (disabled) | 6 | 5.0.1 | 11.00 (disabled) | |||
| April 22, 2011 | 6[23][a] | ||||||
| July 11, 2011 | 7[25][a] | 7 | 14[26] | ||||
| December, 2011 | 10[27] | 11 | 11 | 16[28] | 6 | 12.10[29] | 4.4 |
Protocol handshake[edit]
To establish a WebSocket connection, the client sends a WebSocket handshake request, for which the server returns a WebSocket handshake response, as shown in the example below.[30]
Client request (just like in HTTP, each line ends with \r\n and there must be an extra blank line at the end):
GET /chat HTTP/1.1 Host: server.example.com Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Key: x3JJHMbDL1EzLkh9GBhXDw== Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat, superchat Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13 Origin: http://example.comServer response:
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Accept: HSmrc0sMlYUkAGmm5OPpG2HaGWk= Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chatThe handshake resembles HTTP in allowing servers to handle HTTP connections as well as WebSocket connections on the same port. Once the connection is established, communication switches to a bidirectional binary protocol which doesn't conform to the HTTP protocol.
In addition to Upgrade headers, the client sends a Sec-WebSocket-Key header containing base64-encoded random bytes, and the server replies with a hash of the key in the Sec-WebSocket-Accept header. This is intended to prevent a caching proxy from re-sending a previous WebSocket conversation,[31] and does not provide any authentication, privacy or integrity. The hashing function appends the fixed string 258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11 (a GUID) to the value from Sec-WebSocket-Key header (which is not decoded from base64), applies the SHA-1 hashing function, and encodes the result using base64.[32]
Once the connection is established, the client and server can send WebSocket data or text frames back and forth in full-duplex mode. The data is minimally framed, with a small header followed by payload. WebSocket transmissions are described as "messages", where a single message can optionally be split across several data frames. This can allow for sending of messages where initial data is available but the complete length of the message is unknown (it sends one data frame after another until the end is reached and marked with the FIN bit). With extensions to the protocol, this can also be used for multiplexing several streams simultaneously (for instance to avoid monopolizing use of a socket for a single large payload).
It is important (from a security perspective) to validate the "Origin" header during the connection establishment process on the server side (against the expected origins) to avoid Cross-Site WebSocket Hijacking attacks, which might be possible when the connection is authenticated with Cookies or HTTP authentication. It is better to use tokens or similar protection mechanisms to authenticate the WebSocket connection when sensitive (private) data is being transferred over the WebSocket.[33]
Proxy traversal[edit]
WebSocket protocol client implementations try to detect if the user agent is configured to use a proxy when connecting to destination host and port and, if it is, uses HTTP CONNECT method to set up a persistent tunnel.
While the WebSocket protocol itself is unaware of proxy servers and firewalls, it features an HTTP-compatible handshake thus allowing HTTP servers to share their default HTTP and HTTPS ports (80 and 443) with a WebSocket gateway or server. The WebSocket protocol defines a ws:// and wss:// prefix to indicate a WebSocket and a WebSocket Secure connection, respectively. Both schemes use an HTTP upgrade mechanism to upgrade to the WebSocket protocol. Some proxy servers are transparent and work fine with WebSocket; others will prevent WebSocket from working correctly, causing the connection to fail. In some cases, additional proxy server configuration may be required, and certain proxy servers may need to be upgraded to support WebSocket.
If unencrypted WebSocket traffic flows through an explicit or a transparent proxy server without WebSockets support, the connection will likely fail.[34]
If an encrypted WebSocket connection is used, then the use of Transport Layer Security (TLS) in the WebSocket Secure connection ensures that an HTTP CONNECT command is issued when the browser is configured to use an explicit proxy server. This sets up a tunnel, which provides low-level end-to-end TCP communication through the HTTP proxy, between the WebSocket Secure client and the WebSocket server. In the case of transparent proxy servers, the browser is unaware of the proxy server, so no HTTP CONNECT is sent. However, since the wire traffic is encrypted, intermediate transparent proxy servers may simply allow the encrypted traffic through, so there is a much better chance that the WebSocket connection will succeed if WebSocket Secure is used. Using encryption is not free of resource cost, but often provides the highest success rate since it would be travelling through a secure tunnel.
A mid-2010 draft (version hixie-76) broke compatibility with reverse proxies and gateways by including eight bytes of key data after the headers, but not advertising that data in a Content-Length: 8 header.[35] This data was not forwarded by all intermediates, which could lead to protocol failure. More recent drafts (e.g., hybi-09[36]) put the key data in a Sec-WebSocket-Key header, solving this problem.
See also[edit]
- ^ a b Gecko-based browsers versions 6–10 implement the WebSocket object as "MozWebSocket",[24] requiring extra code to integrate with existing WebSocket-enabled code.
References[edit]
- ^ Ian Fette; Alexey Melnikov (December 2011). "Relationship to TCP and HTTP". RFC 6455 The WebSocket Protocol. IETF. sec. 1.7. doi:10.17487/RFC6455. RFC 6455. https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-1.7.
- ^ "Glossary:WebSockets". Mozilla Developer Network. 2015.
- ^ HTML5 WebSocket: A Quantum Leap in Scalability for the Web
- ^ Graham Klyne, ed. (2011-11-14). "IANA Uniform Resource Identifer (URI) Schemes". Internet Assigned Numbers Authority. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ Ian Fette; Alexey Melnikov (December 2011). "WebSocket URIs". RFC 6455 The WebSocket Protocol. IETF. sec. 3. doi:10.17487/RFC6455. RFC 6455. https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-3.
- ^ Wang, Vanessa; Salim, Frank; Moskovits, Peter (February 2013). "APPENDIX A: WebSocket Frame Inspection with Google Chrome Developer Tools". The Definitive Guide to HTML5 WebSocket. Apress. ISBN 978-1-4302-4740-1. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ^ "HTML 5". www.w3.org. Retrieved 2016-04-17.
- ^ "[whatwg] TCPConnection feedback from Michael Carter on 2008-06-18 (whatwg.org from June 2008)". lists.w3.org. Retrieved 2016-04-17.
- ^ "IRC logs: freenode / #whatwg / 20080618". krijnhoetmer.nl. Retrieved 2016-04-18.
- ^ "Comet Daily » Blog Archive » Independence Day: HTML5 WebSocket Liberates Comet From Hacks". Retrieved 2016-04-17.
- ^ "Web Sockets Now Available In Google Chrome". Chromium Blog. Retrieved 2016-04-17.
- ^ <[email protected]>, Ian Hickson. "The WebSocket protocol". tools.ietf.org. Retrieved 2016-04-17.
- ^ <[email protected]>, Ian Hickson. "The WebSocket protocol". tools.ietf.org. Retrieved 2016-04-17.
- ^ Dirkjan Ochtman (May 27, 2011). "WebSocket enabled in Firefox 6". Mozilla.org. Retrieved 2011-06-30.
- ^ "Chromium Web Platform Status". Retrieved 2011-08-03.
- ^ "WebSockets (Windows)". Microsoft. 2012-09-28. Retrieved 2012-11-07.
- ^ "WebSockets Protocol Test Report". Tavendo.de. 2011-10-27. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ Katie Marsal (November 23, 2010). "Apple adds accelerometer, WebSockets support to Safari in iOS 4.2". AppleInsider.com. Retrieved 2011-05-09.
- ^ "Web Sockets API". BlackBerry. Archived from the original on June 10, 2011. Retrieved 8 July 2011.
- ^ Chris Heilmann (December 8, 2010). "WebSocket disabled in Firefox 4". Hacks.Mozilla.org. Retrieved 2011-05-09.
- ^ Aleksander Aas (December 10, 2010). "Regarding WebSocket". My Opera Blog. Archived from the original on 2010-12-15. Retrieved 2011-05-09.
- ^ "WebSockets (support in Firefox)". developer.mozilla.org. Mozilla Foundation. 2011-09-30. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ "Bug 640003 - WebSockets - upgrade to ietf-06". Mozilla Foundation. 2011-03-08. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ "WebSockets - MDN". developer.mozilla.org. Mozilla Foundation. 2011-09-30. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ "Bug 640003 - WebSockets - upgrade to ietf-07(comment 91)". Mozilla Foundation. 2011-07-22.
- ^ "Chromium bug 64470". code.google.com. Google. 2010-11-25. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ "WebSockets in Windows Consumer Preview". IE Engineering Team. Microsoft. 2012-03-19. Retrieved 2012-07-23.
- ^ "WebKit Changeset 97247: WebSocket: Update WebSocket protocol to hybi-17". trac.webkit.org. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ "A hot Opera 12.50 summer-time snapshot". Opera Developer News. 2012-08-03. Archived from the original on 2012-08-05. Retrieved 2012-08-03.
- ^ Ian Fette; Alexey Melnikov (December 2011). "Protocol Overview". RFC 6455 The WebSocket Protocol. IETF. sec. 1.2. doi:10.17487/RFC6455. RFC 6455. https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-1.2.
- ^ "Main Goal of WebSocket protocol". IETF. Retrieved 25 July 2015. The computation [...] is meant to prevent a caching intermediary from providing a WS-client with a cached WS-server reply without actual interaction with the WS-server.
- ^ Ian Fette; Alexey Melnikov (December 2011). "Opening Handshake". RFC 6455 The WebSocket Protocol. IETF. p. 8. sec. 1.3. doi:10.17487/RFC6455. RFC 6455. https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-1.3.
- ^ Christian Schneider (August 31, 2013). "Cross-Site WebSocket Hijacking (CSWSH)". Web Application Security Blog.
- ^ Peter Lubbers (March 16, 2010). "How Web Sockets Interact With Proxy Servers". Infoq.com. C4Media Inc. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ Willy Tarreau (2010-07-06). "WebSocket -76 is incompatible with HTTP reverse proxies". ietf.org (email). Internet Engineering Task Force. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ^ Ian Fette (June 13, 2011). "Sec-WebSocket-Key". The WebSocket protocol, draft hybi-09. sec. 11.4. https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-hybi-thewebsocketprotocol-09#section-11.4#section-11.4. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
External links[edit]
en.wikipedia.org
WebSockets | MDN
Вебсокеты это продвинутая технология, позволяющая открыть постоянное двунаправленное сетевое соединение между браузером пользователя и сервером. С помощью его API вы можете отправить сообщение на сервер и получить ответ без выполнения http запроса, причем этот процесс будет событийно-управляемым.
See also
Browser compatibility
We're converting our compatibility data into a machine-readable JSON format. This compatibility table still uses the old format, because we haven't yet converted the data it contains. Find out how you can help!
| Version -76 support | 6 | 4.0 (2.0) | Нет | 11.00 (disabled) | 5.0.1 |
| Protocol version 7 support | Нет | 6.0 (6.0)Moz | Нет | Нет | Нет |
| Protocol version 10 support | 14 | 7.0 (7.0)Moz | HTML5 Labs | ? | ? |
| Standard - RFC 6455 Support | 16 | 11.0 (11.0) | 10 | 12.10 | 6.0 |
| Version -76 support | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Protocol version 7 support | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Protocol version 8 support (IETF draft 10) | ? | 7.0 (7.0) | ? | ? | ? |
| Standard - RFC 6455 Support | 16 (Chrome) | 11.0 (11.0) | ? | 12.10 | 6.0 |
Gecko notes
WebSockets support in Firefox is continuing to track the evolving WebSocket specification. Firefox 6 implements version 7 of the underlying protocol, while Firefox 7 implements version 8 (as specified by IETF draft 10). Firefox mobile received WebSocket support in Firefox mobile 7.0.
Gecko 6.0
Prior to Gecko 6.0 (Firefox 6.0 / Thunderbird 6.0 / SeaMonkey 2.3), there was, incorrectly, a WebSocket object that some sites were thinking implied that WebSocket services were not prefixed; this object has been renamed to MozWebSocket.
Gecko 7.0
Starting in Gecko 7.0 (Firefox 7.0 / Thunderbird 7.0 / SeaMonkey 2.4), the network.websocket.max-connections preference is used to determine the maximum number of WebSocket connections that can be open at a time. The default value is 200.
Gecko 8.0
Starting in Gecko 8.0 (Firefox 8.0 / Thunderbird 8.0 / SeaMonkey 2.5), the deflate-stream extension to the WebSocket protocol has been disabled, since it's been deprecated from the specification drafts. This resolves incompatibilities with some sites.
Gecko 11.0
Prior to Gecko 11.0, both incoming and outgoing messages were limited to 16 MB in size. They may now be up to 2 GB in size. Note, however, that memory limitations (especially on mobile devices) make that a theoretical maximum, not a practical one. In reality, transfers of that size will fail on devices that don't have enough memory.
Additionally, ArrayBuffer send and receive support for binary data has been implemented.
Starting in Gecko 11.0, the WebSocket API is no longer prefixed.
Warning: Among other things, a key reason WebSockets was disabled by default in Firefox 4 and 5 is the discovery of a security issue in the protocol's design. This was fixed in Firefox 6 by implementing a newer version of the protocol that corrects the problem.developer.mozilla.org
|
|
..:::Счетчики:::.. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|


